Android wiping BRATA Malware
The malware is called BRATA, which stands for Brazilian Remote Access Tool Android. It began as an Android RAT (remote access tool) and has now developed into a financial malware that targets individuals and businesses all over the world.
BRATA poses as an app security checker and encourages users to install phone's important app upgrades. The language that BRATA asks the user to update is determined by the device's language settings.
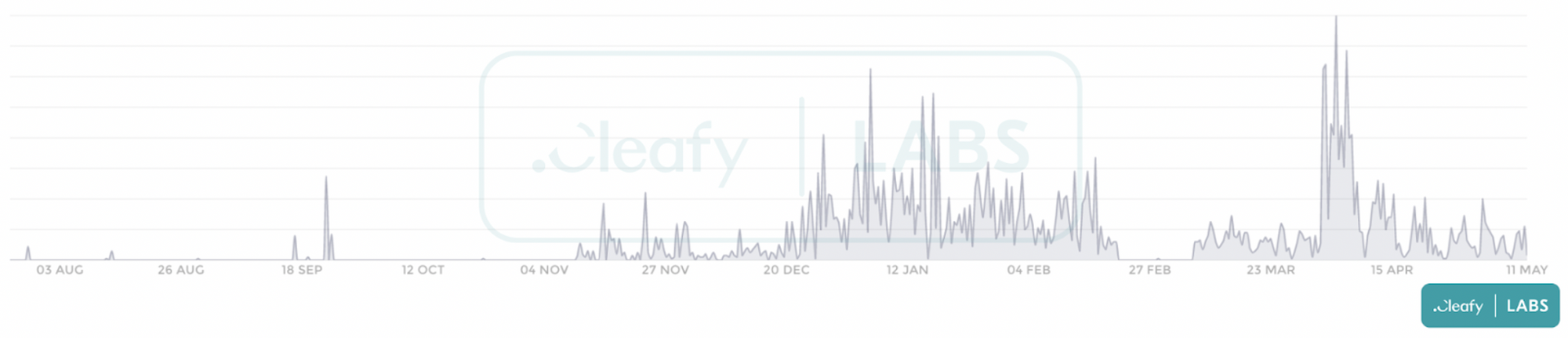
Cleafy in a report this week explains The threat actor behind the BRATA banking trojan has upgraded its techniques and added information-stealing capabilities to the malware. BRATA malware is also more focused since it focuses on one financial institution at a time and only switches to another when defenses render their attacks ineffective.
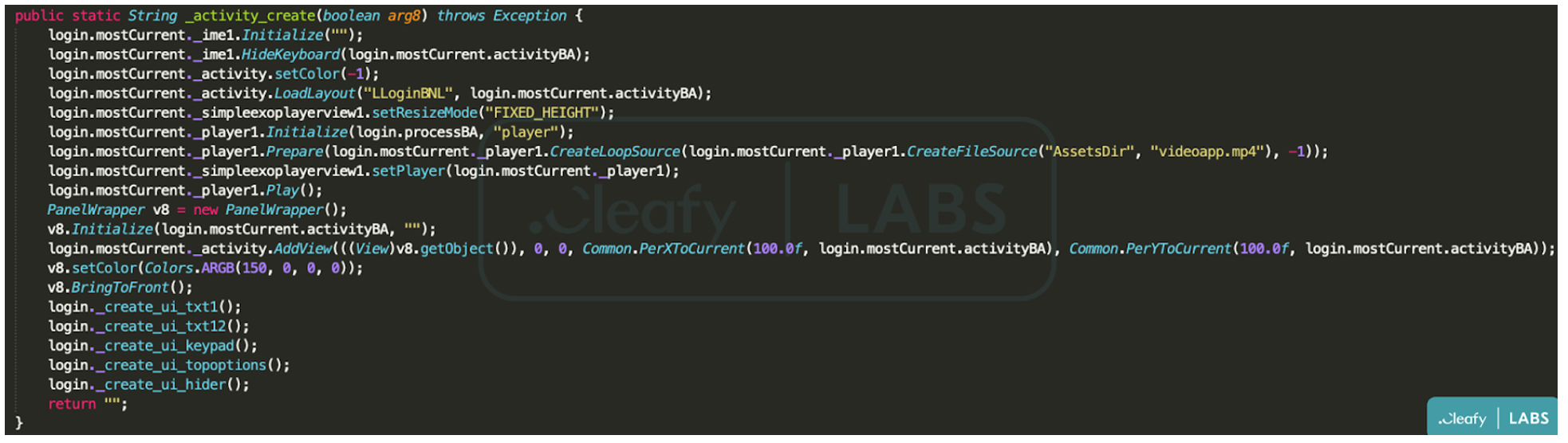
A new version of BRATA has been discovered in the wild, complete with GPS tracking, several C2 communication channels, and customized versions for banking customers in other nations. A factory reset command was also included in that version, which wiped devices clean after all data had been stolen.
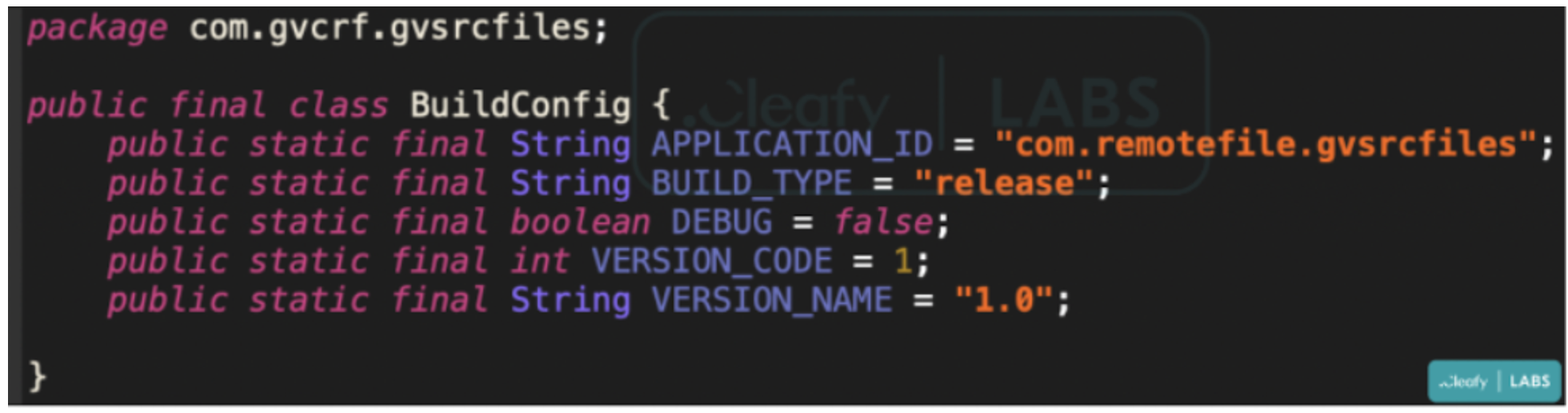
Instead of obtaining a list of installed applications and collecting the appropriate injections from the C2, BRATA now comes pre-loaded with a single phishing overlay. The amount of malicious network traffic and interactions with the host device are reduced as a result. BRATA gains extra rights, including the ability to transmit and receive SMS, which might aid attackers in stealing one-time passwords (OTPs) and two-factor authentication (2FA) tokens that banks send to their clients.
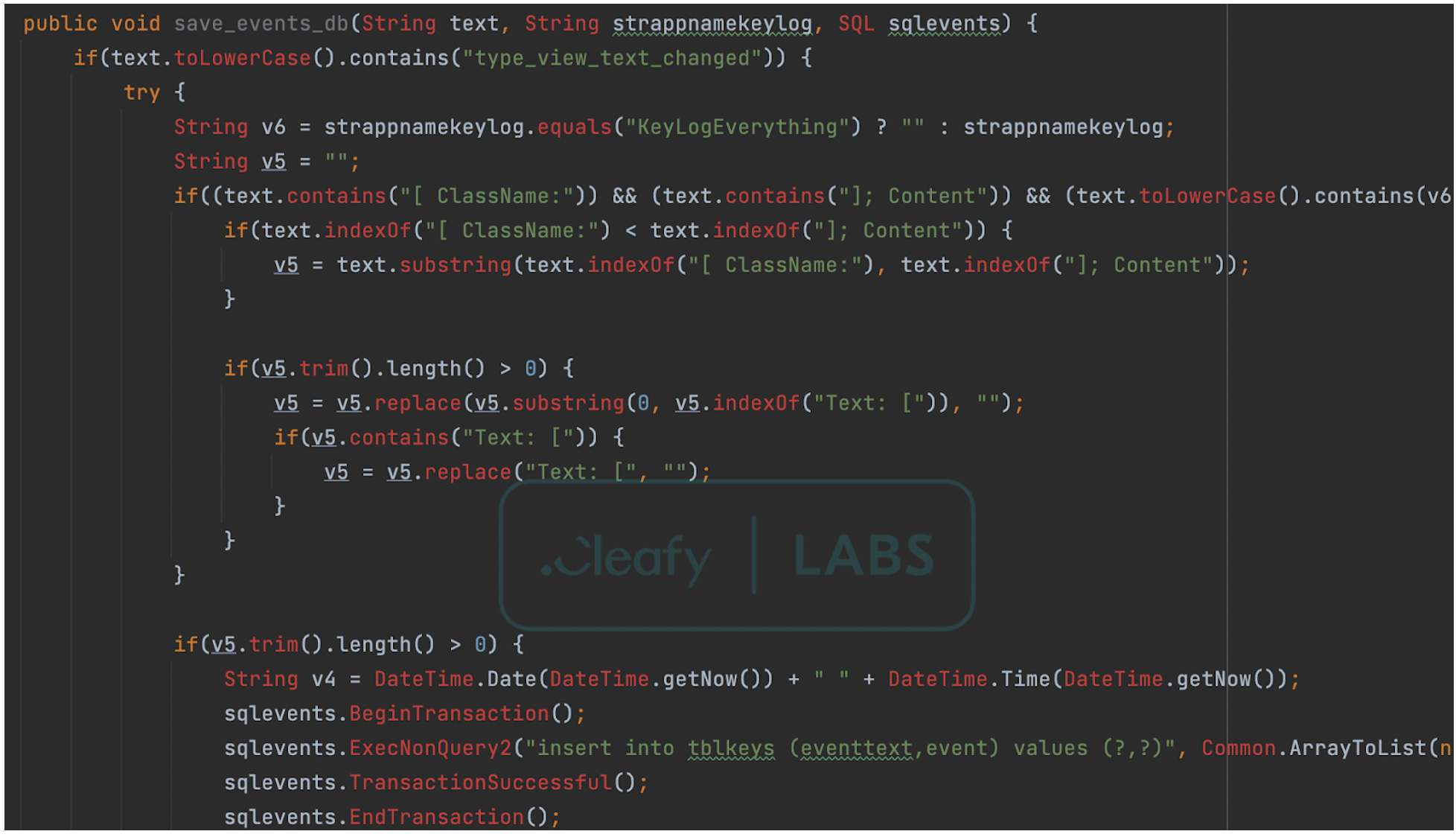
After nesting into a device, BRATA downloads a ZIP archive containing a JAR package from the C2 server. This keylogger keeps track of app-generated events and saves them locally on the device, along with text data and a timestamp.
When BRATA infects a mobile device, it combines full device control with the ability to capture screen lock credentials (PIN, password, or pattern), capture keystrokes (keylogger feature), and record the screen of the compromised device to secretly monitor a user's behavior.
SMS Stealer
During Cleafy analysis of the last BRATA campaign, They found a suspicious app connected to the same BRATA C2 infrastructure. An SMS stealer app that leverages the same C2 infrastructure has been released. It has the same structure and class names as BRATA, but it appears to be focused only on stealing short text messages. The software asks for permission to access the device's contacts and to make it the default messaging app in order to intercept incoming SMS.
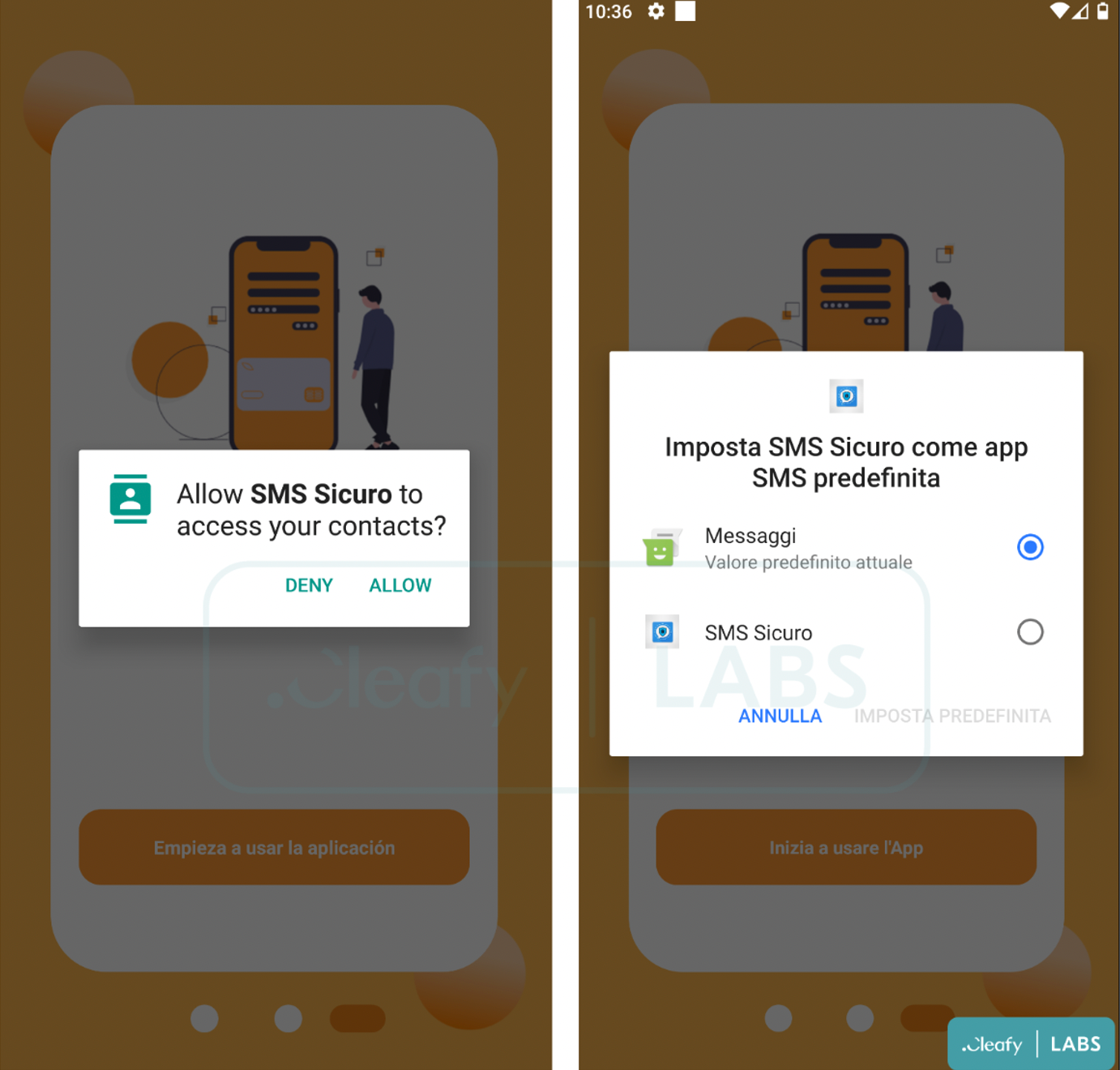
The malicious app seems to target three different countries: Great Britain, Italy, and Spain. During the installation phases, in fact, requires you to choose the language of the app.
Indicator Of Compromise (IOCs)
SHA-256
- 8774dfe8c18fc06d11c81ffedf55a3918e35ba1128f794374458a77c65a1dfb5
- 6978d1a52f097822b44ea2ed941f247faeedfdd95c5a623920cfe877dc08858e
- 102d1425e04997db936460a8b7df1fcb0d5510b51721db9b0de71dc65d0455c6
- eff8594aa83411948b1e2211795f22064dec6b43fab36f08a053fbdda4b8c68f
- fdab91c39c5878226bf8ac39a71558de2da53e23fb7d3ba3b089cc82a37d47fe
- ea68eb1b836677cc00fc4d6104c5f667c5841b34e481ac7903766cd6b04c30b1
- c6c781767025d3ea7b014765ad64fe1b0df0b68cd7d658f4eda5b12b1acfcb4d
- 6efc7d9be4e7f7c139af57784703bfea1ba75277116818742d789fdc19c3568a
- 49438dc8da1cc4882309e381c5e5a36f1fdbc6982de26e7003ff370b80a8dcec
- b11e0b6f5b20aeb60db12053ef249a4aa1894b82227b62316020da4dc7a8ea56
- 2d15bc6c736c5422f3673d94c8f9d3d28ac1512eae6f459cd768842103266937



