A New MacStealer steals a wide range of user data
MacStealer was found by security experts at Uptycs, who noted that it steals a variety of information from the device, including passwords, photos, credit card information, and personal information. Attackers are increasingly turning to it, particularly for stealer command and control (C2).
The Uptycs threat intelligence team's search for the threat actor behind MacStealer led to their discovery. The burglar can take login information, documents, and cookies from the victim's browser. It affects versions of macOS after Catalina that use Intel M1 and M2 CPUs.
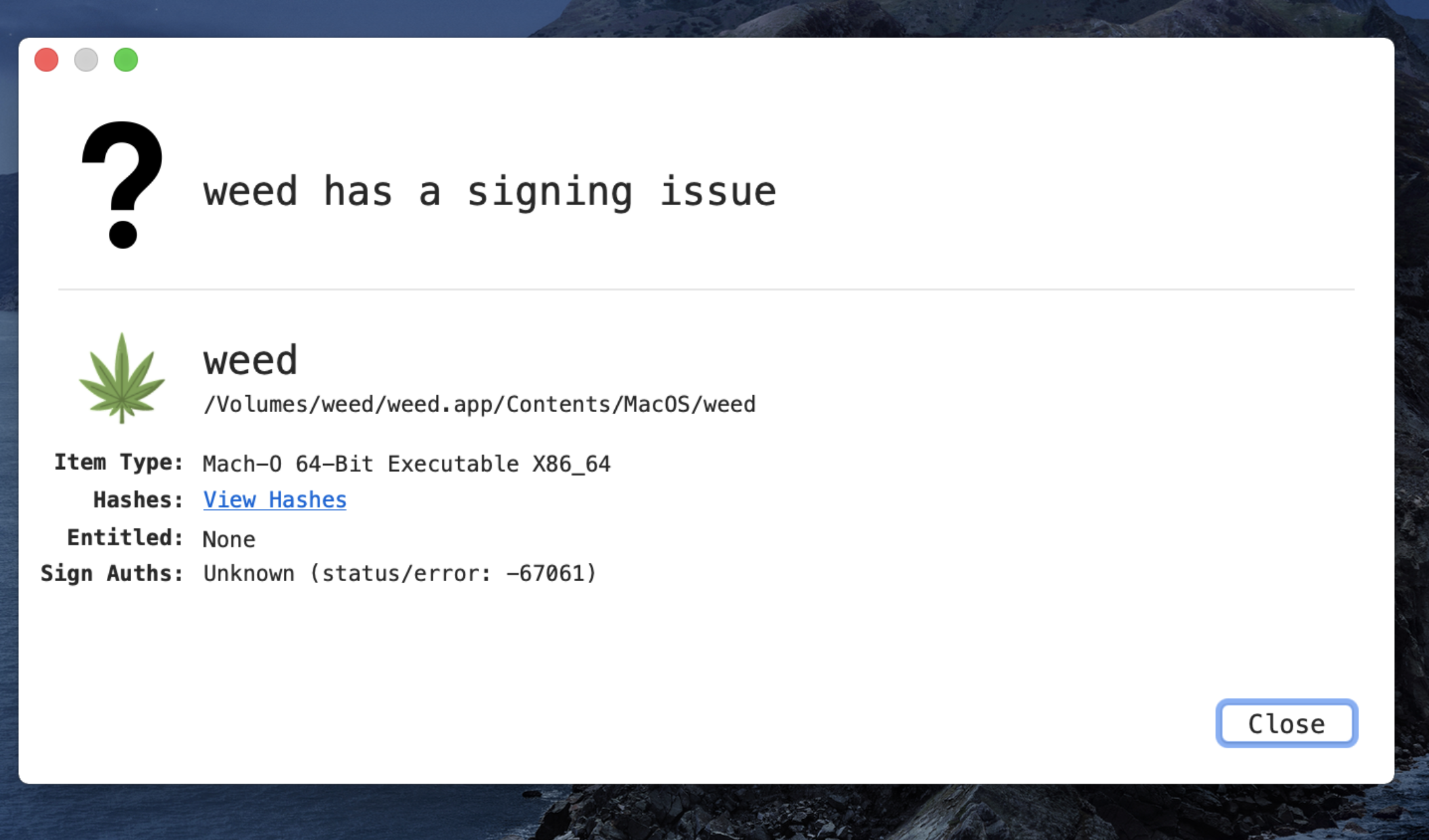
Python code is used to compile the Mach-O file. To transmit the infection, the malicious party uses a.DMG file. When a user runs the file, it opens a phoney password prompt and uses the following command line to collect passwords.
As soon as the user inputs their login information, the stealer begins to collect data in accordance with the features section of the MacStealer. It keeps it in the system directory listed below.
The data is then compressed into a ZIP file and sent to C2 using a POST request with a Python User-Agent request. During a subsequent mop-up procedure, the data and ZIP file are removed from the victim's machine.
Indicators of Compromise
File Hashes (SHA256)
- 9b17aee4c8a5c6e069fbb123578410c0a7f44b438a4c988be2b65ab4296cff5e
- 6a4f8b65a568a779801b72bce215036bea298e2c08ec54906bb3ebbe5c16c712
Domains, URLs & Ip Address
- hxxp[:]//mac[.]cracked23[.]site/uploadLog
- mac[.]cracked23[.]site
- 89[.]116[.]236[.]26
- hxxps[:]//t[.]me/macos_stealer_2023
- hxxps[:]//t[.]me/macos_logsbot



